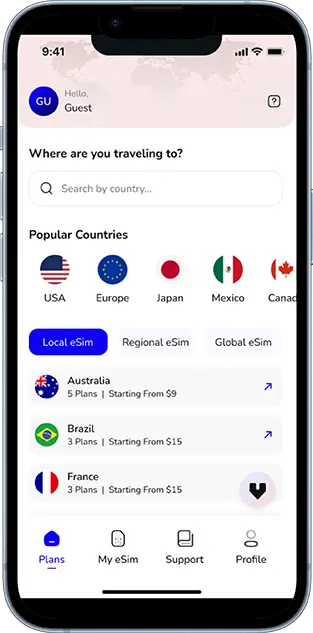
Note that iPhone devices from Mainland China aren’t eSIM compatible. Also iPhone devices from Hong Kong and Macao aren’t compatible (except for iPhone 13 Mini, iPhone 12 Mini, iPhone SE 2020 and iPhone XS)
Understanding mobile connectivity is crucial in a world increasingly dependent on staying connected. Whether you’re streaming your favorite series, sending multimedia messages (MMS), or navigating new destinations with an eSIM, all these activities hinge on one pivotal piece of technology—APN, or Access Point Name.
If you’ve encountered terms like “APN settings” while troubleshooting mobile data issues or optimizing connectivity, this blog is for you. We’ll break down everything you need to know about APN, including what it is, how it works, and why it matters.
Dive in to learn how APN settings can help you stay seamlessly connected, whether you’re a frequent traveler, an IT specialist, or a tech-savvy eSIM user.
Your Journey, Our eSIM
Stay online abroad with instant activation.
What is APN?
APN stands for Access Point Name. Simply put, it’s the gateway that enables your mobile device to communicate with an internet network. Think of the APN as the intermediary that connects your phone or tablet to your carrier’s network so you can use mobile data, send MMS, or access other services without interruption.
Why is APN Important?
Mobile networks rely on APN to route your device’s data. Without it, you wouldn’t be able to browse the web or send emails on the go. Correct APN settings are essential for accessing:
- Mobile data for browsing and app usage
- MMS for sending and receiving multimedia
- Other carrier-specific services, such as Visual Voicemail or tethering capabilities
Critical for both physical SIM and eSIM technology, APN is the linchpin of mobile network configurations that keep you connected.
How Does APN Work?
APN acts as the bridge between your mobile device and your carrier’s broader internet infrastructure. Here’s how it works step by step:
- Network Authentication – When your mobile device tries to establish a connection, it sends a request via its APN settings.
- Gateway Access – The carrier’s network uses this access point to verify the device’s credentials and direct the appropriate data or MMS service.
- Data Routing – If authentication is successful, the network routes your data or message via the correct channels (based on APN settings).
Your device’s APN configurations dictate data speed, reliability, and even access permissions for functionalities like wandering across networks or sending international MMS.
What Are APN Settings?
APN settings are the configurations on your mobile device that contain the necessary information to connect to your carrier’s network. These settings typically include:
- APN Name: Identifies the carrier’s access point.
- Username & Password: Optional credentials for authentication.
- MMSC & MMS Proxy: Specific settings for managing text messages with multimedia components.
- Authentication Type: Determines the security mechanism (e.g., PAP or CHAP).
Devices automatically apply default APN settings when a SIM card is inserted, but users may need to configure them manually in some cases.
Components of APN Settings
To gain a deeper understanding, here’s a breakdown of key APN setting components and their significance:
1. Name
This is the identifier that tells the phone which access point to use (e.g., “Verizon Internet” or “T-Mobile MMS”).
2. APN
The actual URL or address that acts as the gateway.
3. Username & Password
These are optional and used for identity verification where needed.
4. MMSC (Multimedia Messaging Service Center)
This setting manages the sending and receiving of MMS, ensuring multimedia content like videos and photos are transmitted correctly.
5. APN Type
Defines the type of connection, such as:
- `default` for internet browsing
- `mms` for sending multimedia messages
- `supl` for assisted GPS services
6. Authentication Type
Specifies authentication protocols like:
- PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
- CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol)
Configuring these settings correctly ensures seamless mobile internet and MMS experiences.
Why is APN Important?
Key Reasons to Pay Attention to APN Settings
- Seamless Connectivity – Proper APN configurations ensure you have uninterrupted access to mobile data and MMS services.
- Efficient Troubleshooting – APN settings are often the first point of troubleshooting for internet connectivity issues.
- Travel Compatibility – International travelers benefit from personalized APN settings that work with local carriers.
Incorrect APN settings may result in dropped connections, slower internet speeds, or issues sending multimedia.
How to Set or Change APN Settings
Even though many devices auto-configure APN settings for simplicity, there are instances where manual configuration is necessary (e.g., after changing carriers or traveling internationally). Here’s how you can do it:
On an Android Device
- Navigate to Settings > Mobile Networks > Access Point Names.
- Tap Add APN.
- Enter the APN details provided by your carrier.
- Save the settings and restart your device.
On an iOS Device
- Go to Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Options > Cellular Network.
- Input your carrier-provided APN details.
- Save, and restart your device.
When configuring your device, ensure accuracy to avoid disrupted service.
Common APN Issues and Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- No data connection
- MMS not sending/receiving
- Slow data speeds
Troubleshooting Tips
- Reset APN to default settings.
- Double-check configurations with your carrier’s official support page.
- Restart your device after applying changes.
APN and eSIM Technology
With the rise of eSIM technology, APN settings are still critical. Unlike traditional SIM cards, eSIM is embedded in your device, but mobile network configurations (including APN) remain necessary to enable services like mobile data or MMS.
eSIM simplifies international travel by eliminating the need to switch SIM cards, but APN reconfiguration may still be required depending on the carrier.
Best Practices for Managing APN Settings
- Regularly verify your APN settings, especially after changing carriers or traveling.
- Back up your configurations.
- Save custom APN profiles for quick access.
Conclusion
Understanding APN is essential for troubleshooting, optimizing, and improving your mobile connectivity experiences—especially for travelers, IT specialists, and eSIM users. Whether you’re dealing with slow data, MMS issues, or configuring a new carrier on your device, APN settings hold the key to better connectivity.
Take the time to review your APN configurations, and if you’d like to learn more about optimizing mobile network setups or resolving connectivity issues, contact your carrier or IT specialist for guidance.
Global Coverage, Local Rates
Experience hassle-free connectivity wherever you go.
Seamless Mobile Data Everywhere