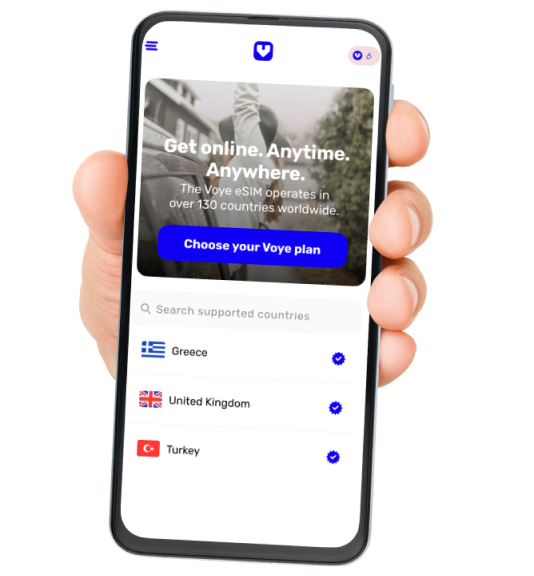
How travel eSIM is superior to traditional physical SIM?
The world is rapidly evolving, and the way we communicate and access data is changing. Traditional physical SIM cards have been the standard for decades, but a new technology called eSIM (embedded SIM) is quickly gaining traction, offering a more convenient and flexible solution for travelers and globetrotters alike. In this blog post, we’ll explore the advantages of eSIM over physical SIM cards, highlighting the benefits, pros, and cons of this innovative technology.
What is eSIM?
Before delving into the advantages of eSIM, let’s first understand what it is. An eSIM is a digital or embedded SIM card that is integrated directly into a device’s hardware, eliminating the need for a physical SIM card slot. This technology allows users to switch between different mobile network operators and data plans without physically swapping out SIM cards.
Benefits of eSIM:
- Seamless Connectivity: One of the most significant advantages of eSIM is the ability to switch between mobile networks and data plans seamlessly, without the hassle of physically removing and inserting a new SIM card. This is particularly beneficial for frequent travelers who need to connect to different networks across multiple countries.
- Space-saving: eSIM technology eliminates the need for a physical SIM card slot, allowing device manufacturers to create sleeker and more compact designs.
- Convenience: With eSIM, users can easily switch between different mobile plans or carriers directly from their device, without the need to visit a physical store or wait for a new SIM card to be delivered.
- Increased Security: eSIM technology offers enhanced security features, as the embedded SIM is more difficult to tamper with or clone compared to traditional physical SIM cards.
Cons of eSIM:
- Limited Compatibility: While eSIM technology is gaining traction, not all devices and mobile networks currently support it, which could limit its adoption in certain regions or for specific use cases.
- Initial Setup: Setting up an eSIM for the first time can be more complex than a physical SIM card, as it may require additional steps or assistance from the mobile network operator.
- Potential Vendor Lock-in: Some device manufacturers or mobile network operators may implement eSIM in a way that limits user choice or creates vendor lock-in scenarios.
- Cost: In some cases, eSIM-enabled devices or plans may be more expensive than their traditional counterparts, at least initially, until the technology becomes more widespread.
Make the Smart Switch
Stay online abroad with instant activation.
eSIM vs. Physical SIM: Pros and Cons
When comparing eSIM to traditional physical SIM cards, the advantages of eSIM become more apparent. Here are some key points to consider:
Pros of eSIM:
- Seamless global connectivity without the need for swapping SIM cards
- Increased convenience and flexibility for frequent travelers
- Space-saving designs and sleeker devices
- Enhanced security features
Cons of Physical SIM:
- Inconvenient for frequent travelers who need to swap SIM cards
- Potential for lost or damaged physical SIM cards
- Limitations in device design due to the need for a SIM card slot
- Increased security risks associated with physical SIM card cloning or theft
The Future of eSIM
As technology continues to evolve, the adoption of eSIM is expected to grow rapidly. Major device manufacturers, such as Apple and Google, have already embraced eSIM technology, and more mobile network operators are offering eSIM-compatible plans and services.
One of the key drivers behind the growth of eSIM is the increasing demand for Internet of Things (IoT) devices and connected gadgets. eSIM technology offers a more efficient and secure way to connect these devices to the internet, without the need for physical SIM card installation.
Furthermore, the integration of eSIM technology into smartphones and other mobile devices is expected to revolutionize the way we purchase and manage our mobile plans. Instead of being tied to a specific carrier or plan, users will have the flexibility to switch between different providers and plans seamlessly, choosing the best option based on their needs and location.
Upgrade Your Connectivity
Ditch the hassle of swapping SIM cards.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving world of technology, eSIM represents a significant step forward in the way we connect and access data. With its advantages of seamless connectivity, space-saving designs, enhanced security, increased convenience, and reduced environmental impact, eSIM is poised to become the future of mobile connectivity, particularly for frequent travelers and those who demand a hassle-free experience. While there are still some limitations and potential drawbacks to consider, the pros of eSIM outweigh the cons, making it a superior choice over traditional physical SIM cards for those seeking a truly global and future-proof solution. As more devices and mobile networks embrace eSIM technology, the benefits will become even more apparent, paving the way for a seamless and connected world.