Note that iPhone devices from Mainland China aren’t eSIM compatible. Also iPhone devices from Hong Kong and Macao aren’t compatible (except for iPhone 13 Mini, iPhone 12 Mini, iPhone SE 2020 and iPhone XS)
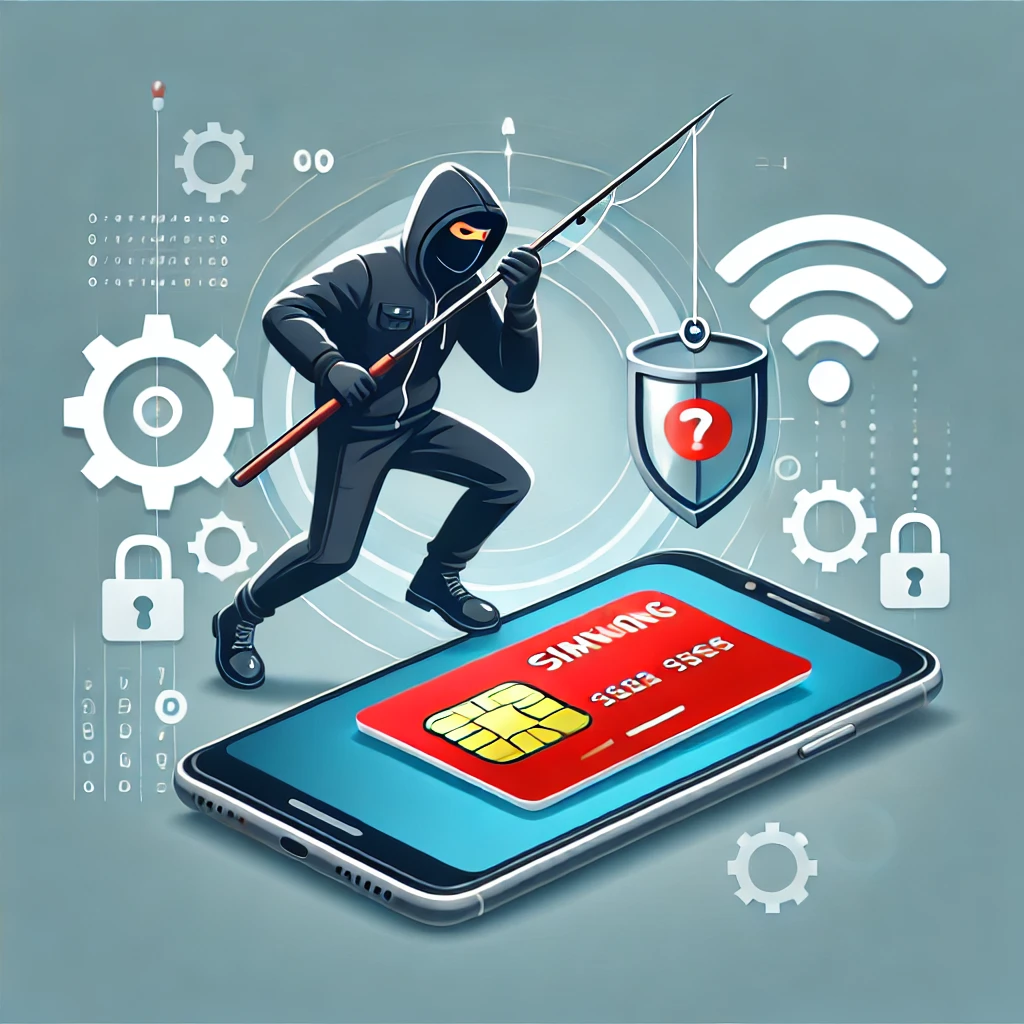
In today’s hyper-connected world, our smartphones are more than just communication tools—they are lifelines to our finances, social networks, and digital identities. At the heart of this connectivity lies a tiny but crucial component: the SIM card. A physical SIM card, or Subscriber Identity Module, is the key that links your device to a mobile network, enabling everything from voice calls and text messages to data usage and authentication services. However, as technology has evolved, so have the tactics of cybercriminals. Increasingly, the physical SIM has become a weak link in mobile security, opening the door to various types of cyberattacks.
This blog explores the security risks associated with physical SIM cards, real-life cases of SIM-based attacks, and why eSIM technology is emerging as a safer, more secure alternative.
What is a Physical SIM Card?
A physical SIM card is a small chip that stores your International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) and encryption keys to securely connect your phone to the mobile network. It’s inserted into your phone and allows your carrier to identify and authenticate your device.
The Role of SIM Cards in Mobile Communication
SIM cards facilitate essential functions such as:
- Making and receiving calls
- Sending and receiving SMS
- Using mobile data
- Enabling secure authentication with network providers
Given this crucial role, the security of SIM cards is paramount. However, their physical nature and limited built-in defenses make them susceptible to various forms of exploitation.
Growing Concerns About SIM-Related Cyber Threats
As mobile phones increasingly serve as gateways to sensitive information—from online banking to social media accounts—cybercriminals are targeting SIM cards to gain unauthorized access. The rise in SIM-related hacks like SIM swapping, SIM cloning, and eavesdropping highlights the urgent need for better mobile security.
Common Security Breaches Involving Physical SIMs
SIM Swapping Attacks
One of the most notorious SIM-based attacks is SIM swapping. Here’s how it works:
- A hacker obtains personal information about the victim through phishing, data leaks, or social engineering.
- They contact the victim’s mobile carrier and impersonate them, claiming their phone was lost or stolen.
- By convincing the carrier to activate a new SIM card, the hacker takes over the victim’s phone number.
Consequences:
- The hacker can bypass two-factor authentication (2FA)
- They can reset passwords and access bank accounts, emails, and social profiles
- Victims often suffer financial losses and identity theft
SIM Cloning
SIM cloning involves duplicating a physical SIM card so that two devices can use the same credentials simultaneously. Hackers use special equipment to extract data from the original SIM, including encryption keys and authentication codes.
Risks Include:
- Intercepted calls and messages
- Unauthorized access to secure apps
- Data leakage and surveillance
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
In some cases, compromised SIMs can be used to intercept or manipulate communication.
- Attackers place themselves between the victim and the network
- They can intercept, alter, or reroute messages and calls
- Often used for espionage or surveillance
Social Engineering Tactics
Cybercriminals often rely on manipulating customer service representatives to execute SIM attacks.
Common Tactics:
- Pretending to be the account holder
- Faking documents or using publicly available personal information
- Exploiting telecom employees via phishing or bribery
Real-Life Cases of SIM-Based Cyber Attacks
Case 1: The Twitter CEO Hack (2019)
In 2019, Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey’s Twitter account was hijacked through a SIM swap attack. Hackers used the access to post offensive tweets to millions of followers.
Impact:
- Damaged reputation
- Highlighted the vulnerability of SMS-based 2FA
Case 2: Cryptocurrency Investor Loses $24 Million
Michael Terpin, a well-known crypto investor, lost $24 million in digital assets due to a SIM swap attack. Hackers transferred his phone number to a new SIM and used it to access his cryptocurrency wallets.
Impact:
- Massive financial loss
- Legal battle with the telecom provider
Case 3: UK Bank Accounts Hacked via SIM Swap
Multiple UK residents reported unauthorized access to their online bank accounts. In each case, attackers used SIM swaps to intercept OTPs (One-Time Passwords) and drain funds.
Impact:
- Bank fraud and loss of savings
- Growing distrust in SMS-based verification
Why eSIM Is a More Secure Alternative?
An eSIM, or embedded SIM, is a reprogrammable chip built into modern smartphones, smartwatches, and tablets. Unlike physical SIMs, eSIMs are activated digitally, eliminating many of the risks associated with traditional SIM cards.
Built-in Encryption and Remote Provisioning
- eSIMs use stronger encryption protocols
- Data is transmitted securely over the air during provisioning
- Less vulnerable to tampering or cloning
No Physical Card to Be Stolen or Swapped
- Cannot be removed or inserted into another device
- Renders SIM swapping attacks nearly impossible
Enhanced Authentication Methods
- Supports advanced security measures like biometric verification
- Can integrate with zero-trust security models for enterprise use
Constant Connectivity Without Physical Handling
- Ideal for frequent travelers and digital nomads
- Eliminates the need to carry or replace physical SIM cards
How to Protect Yourself from SIM-Based Threats?
1. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) with Authenticator Apps
- Avoid using SMS-based 2FA
- Use authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy
2. Use Strong Passwords and PIN Codes for Mobile Accounts
- Set a unique, complex PIN with your telecom provider
- Use password managers to create and store secure passwords
3. Be Cautious of Phishing Scams and Unsolicited Requests
- Do not share personal information via email or text
- Verify contacts before clicking on links or giving out details
4. Monitor Mobile Network Behavior
- Unexpected loss of service may indicate a SIM swap
- Contact your carrier immediately if your phone number stops working
5. Opt for eSIM Technology
- Choose devices that support eSIM activation
- Use trusted providers like Voye Global for secure, international eSIM connectivity
Conclusion: The Future Lies in eSIM Security
The physical SIM card, while foundational to mobile connectivity, has become a significant security liability in the age of digital threats. From SIM swapping and cloning to sophisticated MITM attacks, the risks are too substantial to ignore. Real-world incidents have demonstrated the devastating consequences of SIM-based attacks, affecting individuals, investors, and even tech CEOs.
Fortunately, eSIM technology offers a safer, more resilient alternative. With its built-in encryption, remote provisioning, and immunity to physical tampering, eSIMs mark a turning point in mobile security. By transitioning to eSIM and adopting proactive security measures, users can protect themselves from the dangers of physical SIM cards and embrace a future-proof solution.
Global Coverage, Local Rates
Experience hassle-free connectivity wherever you go.
Seamless Mobile Data Everywhere