Note that iPhone devices from Mainland China aren’t eSIM compatible. Also iPhone devices from Hong Kong and Macao aren’t compatible (except for iPhone 13 Mini, iPhone 12 Mini, iPhone SE 2020 and iPhone XS)
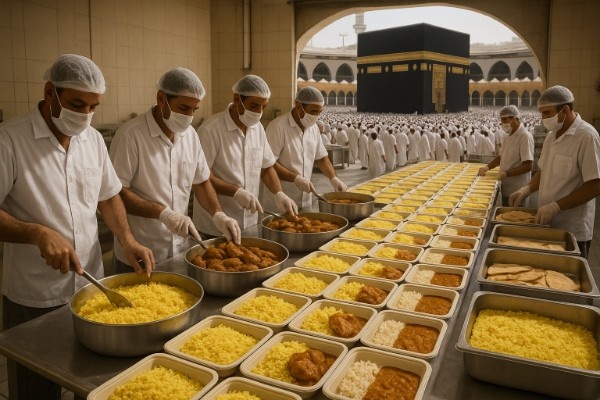
Each year, millions of Muslims from around the world gather in Makkah, Saudi Arabia, to perform the Hajj pilgrimage. As one of the largest and most logistically complex religious gatherings on the planet, Hajj is not only a spiritual journey but also a monumental organizational undertaking. One of the most critical aspects of this operation is ensuring that every pilgrim is adequately nourished—safely, hygienically, and in line with religious dietary requirements.
Feeding the faithful during Hajj is a spiritual and operational feat, combining advanced logistics, large-scale food production, religious sensitivities, and high-volume catering under extreme conditions. In this blog, we dive deep into the intricacies of Hajj catering operations: how meals are planned, produced, delivered, and consumed by over 2 million pilgrims in just a few days.
The Scale of Hajj Catering: Feeding Millions in Motion
During Hajj, pilgrims constantly move between sacred sites—Mina, Arafat, Muzdalifah, and Makkah—over a five-day period. This mobility adds layers of complexity to the catering challenge. On average:
- Over 2 million meals are distributed per day.
- More than 1,000 catering companies and subcontractors are involved.
- Thousands of tons of food and water are procured and transported.
- Meals must adhere to halal standards, regional preferences, and safety protocols.
Catering operations must strike a balance between spiritual service and industrial efficiency—feeding people on a massive scale without compromising quality, ethics, or religious considerations.
Planning the Hajj Menu: Nutrition, Culture & Compliance
1. Halal Compliance and Religious Protocols
All food served during Hajj must be strictly halal, in line with Islamic dietary laws. Catering companies work under the supervision of the Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA) and the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah to ensure:
- Meat is sourced from certified halal suppliers.
- No pork, alcohol, or cross-contamination.
- Food labeling is accurate and compliant.
2. Culturally Diverse Meal Preferences
Pilgrims arrive from over 180 countries, each with distinct culinary preferences. To cater to this diversity:
- Menus are often segmented by nationality or region.
- Popular cuisines include South Asian biryanis, African stews, Turkish rice dishes, and Southeast Asian curries.
- Vegetarian and allergy-friendly options are offered to accommodate health and religious needs.
3. Nutrition in a Harsh Climate
Hajj takes place in the heat of the Arabian desert. Meals must provide hydration, sustenance, and easy digestion:
- High-protein, moderate-carb, and low-oil meals.
- Electrolyte-rich drinks, laban (yogurt drink), and water are essential.
- Fruits and dates are staple additions, as they are sun-stable and energizing.
Planning Hajj logistics?
Stay connected in every holy city with Voye Global eSIM.
The Logistics: From Kitchens to Tents
1. Centralized Cooking Facilities
Large-scale industrial kitchens—some the size of football fields—prepare bulk meals using automation and human labor. These facilities:
- Operate 24/7 during Hajj week.
- Are equipped with industrial ovens, steamers, and blast chillers.
- Prepare over 100,000 meals per shift.
2. Cold Chain and Safe Transport
Food safety is paramount. Saudi authorities mandate:
- Cold chain compliance with temperature monitoring.
- Sealed packaging to avoid contamination.
- Refrigerated trucks for transit between kitchens and pilgrim camps.
3. Last-Mile Delivery
Last-mile catering during Hajj is an art. Meals are delivered via:
- Vans or manual carts inside Mina and Arafat tents.
- Distribution volunteers or company staff trained to manage crowd control.
- QR-coded food labels for tracking and accountability.
Tech and Automation in Hajj Catering
Hajj catering has become increasingly digitized:
- Smart Catering Systems: Software tools plan meal volumes based on pilgrim data, nationality, age, and dietary restrictions.
- Blockchain for Halal Verification: Ensures meat traceability from slaughter to delivery.
- AI-Based Forecasting: Predicts food demand by analyzing heat levels, mobility patterns, and attendance trends.
Some companies use robotic arms for packing lunchboxes, while others rely on IoT sensors in delivery trucks for temperature logging.
Waste Management and Sustainability
Feeding millions inevitably generates waste—but recent Hajj efforts have emphasized:
- Eco-friendly packaging made of biodegradable materials.
- Portion-controlled servings to reduce leftover food.
- Composting and redistribution of untouched food to needy communities post-Hajj.
- Smart bins that monitor food waste in real time for better future planning.
Public Health, Food Safety, and Hygiene
Given the size and heat of the event, foodborne illness prevention is a critical focus:
- All catering staff undergo health checks and hygiene training.
- Kitchens are audited by the Saudi Ministry of Health and the SFDA.
- Random testing of food samples occurs daily during Hajj week.
- Personal protective gear, disinfectant usage, and pest control are mandatory.
Case Study: How a Single Catering Company Operates During Hajj
Take the example of Al-Tazaj Hajj Catering Group, one of the certified operators:
- Staff: 1,200+
- Kitchens: 4 mega-units near Mina and Makkah
- Meals/day: 300,000
- Fleet: 150 refrigerated vehicles
- Menu: Rice, chicken, lentils, bread, yogurt, and water packs
- Quality Assurance: In-house microbiology labs, RFID-tagged food crates
This level of scale is repeated across hundreds of vendors, with coordination led by the National Hajj Commission and the Saudi Catering and Hospitality Authority.
Pilgrim Experiences: What It Feels Like to Be Fed During Hajj
Many pilgrims express gratitude for the seamlessness of food availability during such an intense journey. Despite the size and crowd:
- Meals are delivered with precision.
- Water and hydration booths are widely accessible.
- Volunteer-led distribution adds a spiritual, human touch.
One pilgrim from Indonesia shared:
“The food came like clockwork, and every meal reminded me that this journey is not just physical—it’s divine hospitality at scale.”
Challenges in Hajj Catering Operations
Despite innovation, many challenges persist:
- Sudden demand spikes due to temperature or delayed pilgrim movement.
- Pilgrim dissatisfaction due to unfamiliar cuisine.
- Spoilage and food waste under harsh climate conditions.
- Language barriers between international pilgrims and local staff.
Ongoing reforms aim to digitize more parts of the catering workflow to mitigate these issues.
eSIM Connectivity for Catering Teams and Pilgrims
In such a dynamic, high-pressure environment, reliable communication is key:
- Catering teams use mobile apps to track deliveries, inventory, and staff movement.
- Pilgrims use smartphones for meal location alerts, halal certifications, and reporting concerns.
This makes digital connectivity critical. Voye Global’s eSIM for Saudi Arabia provides:
- Instant data activation upon arrival
- Reliable coverage across all Hajj zones
- Support for delivery staff and pilgrims alike, without the need for a physical SIM
Stay connected to streamline operations and access essential information without disruptions.
Conclusion: Nourishing the Soul and the Body
Feeding the faithful during Hajj is far more than a logistics challenge—it is a sacred responsibility. It requires the collaboration of technology, tradition, religious sensitivity, and human compassion. From halal sourcing and culturally familiar recipes to eco-friendly waste management and seamless food delivery, Hajj catering operations represent the intersection of faith and infrastructure.
As the world looks ahead to smarter pilgrimages, the lessons learned from feeding millions in a few sacred days offer insights into how humanity can serve both spirit and stomach—efficiently, ethically, and reverently.
Traveling for Hajj?
Choose seamless data access with Voye Global’s eSIM for uninterrupted coordination.
Seamless Mobile Data Everywhere