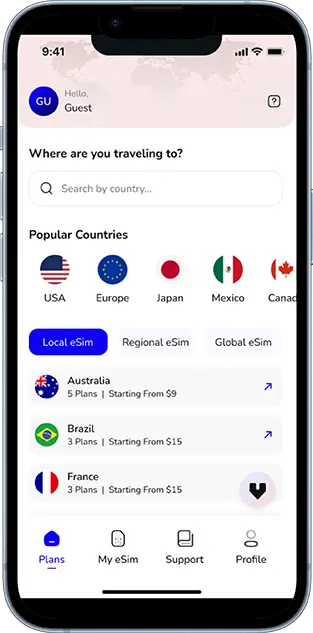
Note that iPhone devices from Mainland China aren’t eSIM compatible. Also iPhone devices from Hong Kong and Macao aren’t compatible (except for iPhone 13 Mini, iPhone 12 Mini, iPhone SE 2020 and iPhone XS)
The evolution of SIM card technology has revolutionized the way we connect to mobile networks. With the advent of eSIM technology, this transformation has reached a new pinnacle. eSIMs, or embedded SIMs, are reshaping the mobile connectivity landscape by eliminating the need for physical SIM cards. This guide dives deep into the various kinds of eSIMs, their unique applications, and how they are enhancing connectivity across different domains.
What is an eSIM?
An eSIM (embedded SIM) is a digital SIM card integrated into devices, enabling connectivity without the need for a physical SIM card. Unlike traditional SIM cards, eSIMs are rewritable and can store multiple profiles, making them highly versatile.
Key Features of eSIM Technology:
- Built directly into devices.
- Allows remote provisioning.
- Supports multiple network profiles.
- Enhances device design and security.
Types of eSIMs and Their Applications
1. Consumer eSIMs
Consumer eSIMs are designed for personal devices like smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. They allow users to switch carriers, activate plans, and manage profiles with ease.
Key Devices Supporting Consumer eSIMs:
- Smartphones: iPhone 14, Google Pixel series, Samsung Galaxy S series.
- Tablets: iPad Pro, Microsoft Surface Pro.
- Smartwatches: Apple Watch, Samsung Galaxy Watch.
Benefits:
- Enables dual-SIM functionality without additional hardware.
- Simplifies travel with seamless carrier switching.
- Reduces the need for physical SIM replacements.
2. IoT eSIMs
The Internet of Things (IoT) relies heavily on connectivity, and IoT eSIMs are specifically designed to support this domain. These eSIMs cater to smart devices like sensors, vehicles, and industrial equipment.
Applications in IoT:
- Smart Cities: Traffic monitoring systems, smart streetlights.
- Connected Vehicles: Autonomous driving, vehicle telematics.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring, wearable medical devices.
- Agriculture: Precision farming, drone-based crop management.
Benefits:
- Allows scalability for millions of connected devices.
- Remote provisioning streamlines deployment.
- Enhances connectivity in remote or dynamic environments.
3. Travel eSIMs
Travel eSIMs are a boon for international travelers who want affordable and hassle-free connectivity. These eSIMs allow users to activate short-term plans tailored to their destinations.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple countries with a single eSIM.
- Eliminates the need for local physical SIMs.
- Offers competitive pricing for data plans.
Benefits:
- Saves money on international roaming charges.
- Provides instant activation without visiting stores.
- Ensures uninterrupted connectivity during travel.
4. Enterprise eSIMs
Enterprise eSIMs cater to business requirements, allowing organizations to manage connectivity for their workforce seamlessly.
Applications:
- Employee smartphones with managed connectivity.
- Laptops with integrated eSIMs for remote work.
- Devices used for field operations like logistics and maintenance.
Benefits:
- Centralized management of connectivity profiles.
- Simplifies provisioning for large teams.
- Ensures secure and reliable connectivity for enterprise applications.
5. Machine-to-Machine (M2M) eSIMs
M2M eSIMs are a subset of IoT eSIMs, designed specifically for machine communication. These eSIMs are widely used in industries requiring robust, long-term connectivity.
Applications:
- Industrial automation systems.
- Energy grids and utility management.
- Fleet management and asset tracking.
Benefits:
- Resilient to harsh environments.
- Remote updates reduce maintenance costs.
- Supports uninterrupted global connectivity.
6. Wearable eSIMs
Wearable devices like fitness trackers and smart glasses are becoming increasingly common, and eSIMs are a perfect fit for these compact gadgets.
Popular Devices with Wearable eSIMs:
- Apple Watch Series.
- Samsung Galaxy Watch.
- Huawei Watch models.
Benefits:
- Compact design without the need for SIM slots.
- Always-on connectivity for health monitoring and notifications.
- Improved integration with smartphones.
7. Embedded Automotive eSIMs
Modern vehicles are becoming smarter with built-in connectivity powered by automotive eSIMs.
Applications in Vehicles:
- In-car entertainment systems.
- Navigation with real-time traffic updates.
- Emergency calling (eCall).
Benefits:
- Improves driving safety and convenience.
- Enables over-the-air updates for software.
- Offers global connectivity for cross-border travel.
How to Choose the Right eSIM?
When selecting an eSIM, consider the following factors:
- Device Compatibility: Ensure your device supports eSIM technology.
- Purpose of Use: Identify whether it’s for personal, travel, enterprise, or IoT use.
- Network Support: Check carrier compatibility in your region or travel destination.
- Pricing Plans: Compare plans for affordability and coverage.
- Flexibility: Choose providers offering multiple profiles and global coverage.
The Future of eSIM Technology
The adoption of eSIMs is accelerating across industries, driven by their versatility and cost-efficiency. As 5G networks expand globally, eSIM technology will become even more crucial in supporting high-speed, low-latency connectivity.
Emerging Trends:
- Integration into more consumer devices.
- Enhanced security features for sensitive applications like banking.
- Widespread adoption in autonomous systems and smart cities.
Conclusion
eSIM technology is redefining connectivity across various domains, offering unparalleled convenience and efficiency. From smartphones and wearables to IoT and automotive applications, the possibilities are endless. By understanding the different types of eSIMs and their applications, you can make informed decisions to leverage this revolutionary technology.
Experience seamless global connectivity with eSIM today and unlock the potential of your devices!
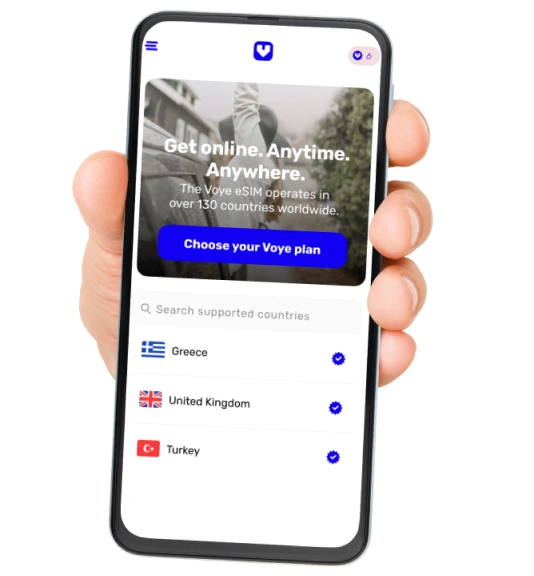
Your Journey, Our eSIM
Stay online abroad with instant activation.
Seamless Mobile Data Everywhere