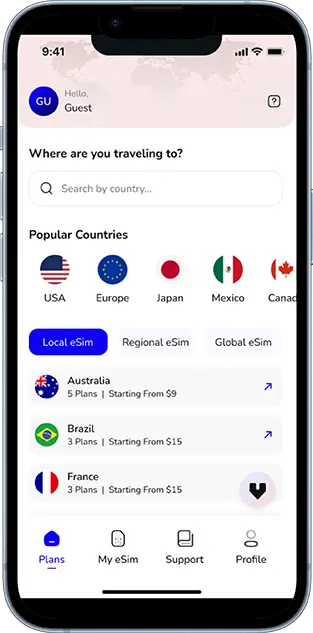
Note that iPhone devices from Mainland China aren’t eSIM compatible. Also iPhone devices from Hong Kong and Macao aren’t compatible (except for iPhone 13 Mini, iPhone 12 Mini, iPhone SE 2020 and iPhone XS)
With the rise of embedded SIM (eSIM) technology, many users are curious about its implications for security, privacy, and tracking. Whether you’re a frequent traveler, a business professional, or someone who values digital privacy, understanding how eSIMs interact with tracking mechanisms is essential.
In this blog, we will explore whether eSIMs can be tracked, how they compare to traditional SIM cards, and what steps you can take to safeguard your data and location.
What is an eSIM?
An eSIM (embedded SIM) is a digital SIM that allows users to activate a cellular plan without a physical SIM card. Unlike traditional SIM cards, which need to be inserted and removed from a phone manually, eSIMs are embedded within a device and can be activated remotely.
How eSIMs Work?
eSIMs store carrier information digitally, enabling users to switch between networks easily. They are rewritable, allowing multiple carrier profiles to exist on a single device. This flexibility is particularly useful for frequent travelers who require seamless connectivity across different countries.
Can eSIMs Be Tracked?
The short answer is yes—just like traditional SIM cards, eSIMs can be tracked under certain circumstances. However, tracking depends on several factors, including the type of tracking being used, the authority or entity conducting the tracking, and the privacy settings enabled by the user.
Here are the primary ways an eSIM can be tracked:
1. Carrier Network Tracking
Mobile network operators (MNOs) track all active SIMs, including eSIMs, for operational purposes. This tracking is necessary to:
- Provide seamless connectivity
- Ensure network security
- Monitor service usage for billing purposes
- Detect fraudulent activities
Every time your eSIM connects to a cellular network, it registers with the nearest cell tower. This process allows carriers to determine your approximate location based on triangulation—the method of analyzing signals from multiple towers.
2. IMEI-Based Tracking
Each smartphone has a unique International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number. Regardless of whether a device uses an eSIM or a physical SIM, authorities and service providers can track it using this identifier. IMEI-based tracking is commonly used in:
- Recovering stolen or lost phones
- Identifying and blacklisting devices for security reasons
- Law enforcement investigations
Since the IMEI is tied to the hardware rather than the SIM itself, switching to a different eSIM profile does not prevent tracking via IMEI.
3. GPS Tracking & Location Services
If location services are enabled on your smartphone, apps and websites can determine your location using GPS, Wi-Fi networks, and Bluetooth signals. While this method does not directly depend on an eSIM, your mobile data connection (provided via eSIM) can still be used to relay location-based information.
Many apps, including Google Maps, Uber, and social media platforms, use GPS tracking to enhance functionality. Users concerned about privacy should regularly review and adjust their location settings.
4. Government & Law Enforcement Surveillance
Governments can request user data from network providers for national security or legal investigations. Just as with traditional SIMs, law enforcement agencies can track eSIM activity through:
- Cell tower data: Identifying approximate location based on signal reception.
- Call and message records: Monitoring call logs and message history.
- Internet activity tracking: Examining data usage patterns via ISP collaboration.
5. Cybersecurity Threats & Unauthorized Tracking
While network-based tracking is legal and generally well-regulated, unauthorized tracking can occur through:
- Spyware & Malware: Malicious software installed on a device can transmit location data to third parties.
- Phishing Attacks: Fraudsters may trick users into revealing sensitive data that can be used for tracking.
- Compromised Apps: Some apps request excessive permissions and secretly collect user location data.
To prevent unauthorized tracking, always update your device, avoid clicking suspicious links, and be cautious about app permissions.
How eSIMs Enhance Privacy Compared to Traditional SIMs?
While eSIMs can be tracked just like traditional SIM cards, they also offer certain privacy advantages:
1. No Physical SIM Card to Trace
Unlike traditional SIMs, eSIMs do not have a removable physical component, reducing the risk of SIM swapping fraud—a common scam where fraudsters steal a victim’s number to gain access to personal accounts.
2. Remote Activation & Deactivation
Users can activate and deactivate eSIMs remotely without needing a new physical card. This feature adds a layer of control, allowing users to remove a compromised eSIM profile instantly.
3. Multiple Profiles for Greater Anonymity
With an eSIM, users can switch between different carrier profiles. While this does not prevent tracking by network operators, it can make it harder for unauthorized entities to monitor long-term location patterns.
4. More Secure Authentication Methods
Many eSIM providers implement stronger authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication (2FA) and eKYC (electronic Know Your Customer) verification. These security measures reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
How to Minimize eSIM Tracking Risks?
If you are concerned about tracking and privacy, consider the following measures:
1. Disable Location Services When Not in Use
Most tracking relies on location services enabled on your phone. You can minimize tracking by:
- Turning off GPS when not needed
- Disabling Wi-Fi and Bluetooth scanning
- Adjusting app permissions to limit location access
2. Use a VPN for Online Privacy
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic, making it harder for ISPs and hackers to track your online activity. While this does not prevent network-based tracking, it enhances digital privacy.
3. Regularly Change eSIM Profiles
If your device supports multiple eSIM profiles, you can periodically switch networks to make it harder for third parties to track long-term movement patterns.
4. Avoid Suspicious Apps & Links
Be cautious about the apps you install and the links you click. Only download apps from trusted sources like Google Play Store or the Apple App Store.
5. Use Airplane Mode When Needed
When you don’t need network connectivity, enable Airplane Mode to temporarily disable all mobile network connections. This will prevent tracking via cell towers.
Conclusion: Should You Worry About eSIM Tracking?
eSIMs can be tracked just like traditional SIM cards, primarily through carrier networks, IMEI tracking, and GPS-based location services. However, they also provide enhanced security and flexibility, making them a reliable option for travelers and privacy-conscious users.
If you’re concerned about being tracked, taking proactive security measures—such as disabling location services, using a VPN, and being cautious with apps—can help safeguard your privacy.
With proper precautions, eSIM technology remains a convenient, secure, and flexible choice for global connectivity. Whether you’re a frequent traveler or simply looking for a hassle-free mobile experience, eSIMs offer great advantages while maintaining a balance between accessibility and security.
Final Thoughts
As technology continues to evolve, privacy concerns will always be a topic of discussion. The best approach is to stay informed, understand how tracking works, and make adjustments that align with your personal security preferences.
Would you like to explore secure eSIM plans for your travels? Check out Voye Global for reliable and affordable eSIM solutions worldwide.
Global Coverage, Local Rates
Experience hassle-free connectivity wherever you go.
Seamless Mobile Data Everywhere